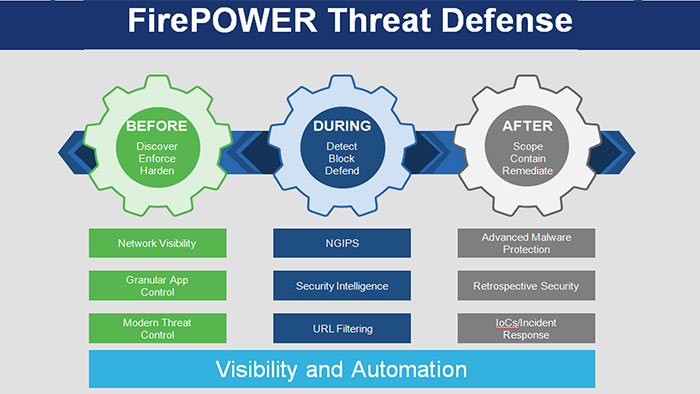
Cisco Secure portfolio is consisted of various range of devices assisting enterprises to provide needed security considerations within their networks. Cisco Secure Firewalls (Formerly Cisco Firepower) are the NGFWs using their powerful built-in Cisco FTD features to provide security along consistency and without speed reduction in the networks. In this article we are going to investigate the following Cisco FTD features which can be managed by Cisco FMC and FDM.

Basically, Cisco Firepower Threat Defense Access Control Policy is an ACL or Access Control List, which binds all of your policies together. You can use the following policies in order to cover different scenarios in your network:
In the FTD individual rules can be placed within the categories for easier and more intuitive management. You can also use the following as optional matches:
You can also benefit from several rule actions to consider what to do when there is a match available:
Actually, the pre-filter policy is the first line of defense for your network and essentially, it will be set on the interface level. Plus, it is effectively an ACL. The pre-filter policy is needed to be set to drop as much as possible traffics. For example, you can drop any telnet connection into your network devices using pre-filter policy, because simply, there is no further inspection needed in this kind of traffic.
The following rule types are available for pre-filter policies:
Also, the pre-filter rule can match on typical objects like interface, VLAN tag and port. Plus, you are able to perform the below actions based on the matches:
Finally, if the logging is needed, it must be explicitly turned on for each rule.
Basically, the discovery is a process used to help to figure out what is running on your network. Gaining this knowledge will provide you the ability to create policies based on what is discovered. Cisco Firepower analyzes all the traffic and can be used to determine the device type such as iPad or Windows PC, the user, and the application. This can be very granular and data collector is extremely valuable.
Cisco secure firewalls use SNORT for intrusion prevention purposes. Basically, SNORT is a collection of many different rules that can match on known malicious traffic patterns. Also, the intrusion processes are highly resource intensive and one of every security admin’s goals is to limit the scope to ensure the services run optimally. Moreover, in addition to optimizing the rules, you have to consider where the rules should even run. This is where the variable sets come to play.
The variable set is designed to help the IPS know the details of your network. So, the IPS uses the predefined variables which help the system determine which traffic should be inspected. For example, a variable named HTTP_PORTS is a collection of all ports associated with HTTP traffic. If the IPS has a rule that only applies to HTTP traffic, it will use the HTTP_PORTS variable to match the traffic to the rule.

First thing for Setting up the IPS using Cisco FMC, is to define IPS base policy. Essentially, there are five options available:
Generally, in Firepower there are fewer rules than traditional IPS and it’s easier to use and understand. FTD will use the following rule states when faces the abnormality in the network:
For most organizations, the intrusion policy is built and put into production with option “Drop when Inline” unchecked. This option causes the rules to be run and generates logs, but no actual traffic will be dropped. This allows you to observe what would have been dropped in real-time experience. After some time of collecting logs and data, Firepower also has a recommendation engine suggesting best rules and policies based on your network traffic. After a while, based on analyzed traffics and triggered events, you can either update the recommendations or turn on “enforcement”.
Finally, when it comes to IPS, optimization is the key value. You should not enable every rules, as a significant amount of traffic will be dropped and performance will be dismal. During the test phase, be sure to analyze all generated events, because there will be false-positive than you may want to disable or change the state of various rules. When in doubt, use the Firepower recommendations. They are not perfectly optimized, but it will provide you a good start if you are new to Intrusion Prevention.
This policy can be used to restrict certain types of files, regardless of whether or not they contain Malwares, and to monitor activities for auditing purposes. These policies use several methods to determine if a file contains Malware, using AMP cloud. Also, these policies are easy to configure, but difficult to fully understand.
Furthermore, every file that flows through Firepower and has a file type assigned to a rule, is a sign of disposition. In disposition, Malware means that the file contains Malware, “Clean” means the file does not contain Malware, Unknown means that the AMP Cloud was unable to categorize the file, Custom Detection means that a manual action was taken to categorize the file and finally, Unavailable means that the AMP Cloud was unavailable.
Moreover, there are following rules available that Firepower maintains whether or not a file is a threat:
For Malware and file configuration purposes, you can apply specific policy only to a specific protocol like SMTP, HTTP and etc. Also, the direction of transfer is ether upload or download. After that, you can consider one of following actions for the file:
So, within an action there are few of other associated options available. When you choose Detect for the action, you can also store a copy of the file. These option required a lot of space available which you must consider that. In using Block option, you can also store the file and reset connection. You can also associate the Local Malware, Dynamic and Spero Analysis, with these options.

Cisco FTD DNS policy comes to play when there is a website with malicious content that Cisco TALOS and other organizations can detect the IP address very quickly. However, the website owner can change the IP address frequently getting around the IP blacklist. But the domain typically does not change which makes it much more difficult to get around the DNS blacklists. That is where DNS filtering comes into play. Instead of blocking IP addresses, Cisco Firepower can intercept the end user DNS query for various domains and stop the traffic before it even starts.
There are many published DNS blacklists that can be used with Firepower. Although, the primary lists are published by Cisco TALOS. Cisco TALOS provides several lists for specific threats like DNS attackers, DNS bots and etc. In overall, blacklist manually maintained simple list of websites that should be blocked while whitelist overrides the DNS lists and permits access.
The following DNS Actions happen when we are willing to happen when the DNS entries are flagged:
This policy is used to determine the actual end user identity rather than a just IP address. It can be used for monitoring user activities in actual policy. Generally, there are two ways for determining end user: Active Authentication and Passive Authentication. Passive authentication is less accurate and Firepower uses this type to identify the end user. In active authentication, Cisco Secure Firewall forwards the user to a portal page and force them to login. Firepower can use the following methods to identify the users:
The following fields must be configured for this matter:
Within the Realm you must also choose an AD/LDAP Server and Firepower must download the users before identity can be used. By default, Realm is disabled, so you need to enable it first.
The Identity source specifies how Firepower will be updated user information changes. In this regard, Cisco ISE uses pxGrid and automatically updates Firepower’s about IP address, pxGrid Server CA, MnT Server and FMC Certificate when the user logins into the network. After all of this, Identity Policy ties all the information together and will provide the following actions:
Moreover, the Match Criteria can be based on the zones, networks, VLAN tags and ports. You also have to choose the Realm and attach the identity policy to the Access Control Policy. Please note that, if you choose active authentication, you can exempt specific applications from requiring active authentication.
SSL policy is required to inspect encrypted traffic. However, it is important to understand that there are some legal and ethical questions that should be resolved prior to implementation. Applying this policy can get complicated with different policies for different policies for different types of encryption. This matter requires the endpoint to trust the CA certification used by Firepower to decrypt/encrypt traffic.
You can manually disallow and blacklist URLs with any license type. The Cisco URL filtering license is only required if you want to use automated lists. There are two criteria that comes to the play. First, the category of the website. There are many categories that you can choose from and the ready to go list are available. Second, reputation is the second criteria with the 1 to 5 score which 1 means very high risk and 5 means well known. You may need to block poor reputation or gamble or alcohol related websites.
There are also situations where you want to hedge against a website that is blocked, but may have a legitimate business purpose. An interactive block allows the user to acknowledge the risk and to proceed anyway.
The security intelligence is designed to block malicious content very early in the inspection process. This feature filters out all obvious threats before the more resource intensive inspection again. Cisco constantly provides and updates the feeds for threats very quickly. Also, by using security intelligence blocks IP addresses, URLs, and domain names based on reputation and occurs before any other filtering methods like DNS, URL, IPS and etc.
Cisco FTD recognizes various applications and can be used to filter or monitor the applications and prevents malicious content from masquerading as a legitimate application. The applications filtering happens based on individual application and overall category, the risk that application represents and the business relevant application or the combination of all.
By using Cisco AnyConnect features, customers can manage their remote connections. Since, FMC version 7, either RADIUS servers such as AD and LDAP. and LOCAL user groups are supported.