
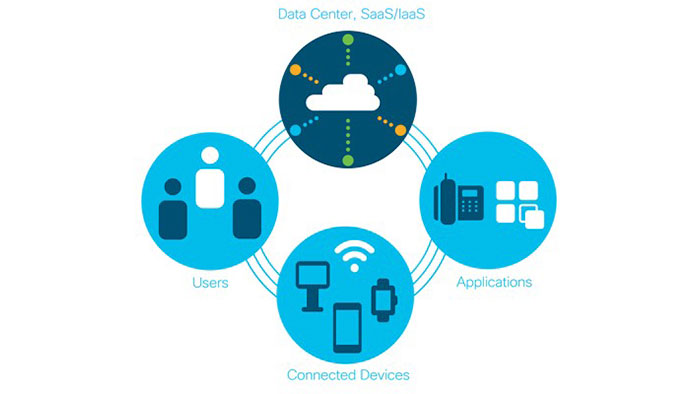
SD-WAN, or software-defined wide area network, is a virtual wide area network that allows organizations to use any desired combination of data transmission services anywhere to connect users to applications. These data transfer services include MPLS, LTE and Internet that includes Cisco vManage.
Traditional wide area network infrastructure was suitable as long as the main flow of traffic within an organization flows within that organization’s intranet. With the passage of time and the growth of cloud service technology and applications under the cloud or SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) such as Office365 and Dropbox, cloud infrastructure or “Infrastructure as a Service” which is abbreviated as IaaS, such as Microsoft Azure Amazon AWS and Google Cloud, and private clouds such as Cisco Webex accounted for more traffic.
So now the main stream of traffic within many organizations has moved towards public Clouds and the Internet, and in the near future many other organizations will be forced to use such services. These changes have led to the emergence of new needs in the field of security, performance of applications, cloud connections, management and operations.
Traditional wide area network technology was designed to physically connect branches, data centers and the main office of an organization. Unfortunately, this technology has not been able to fully adapt to the changes and developments of today’s modern networks and has faced challenges:
Today, traditional wide area network technologies are unable to address these dynamic environments and new traffic patterns. As a result, it becomes increasingly difficult to estimate the needs and expectations of users and network administrators in terms of connectivity, application performance, and security. As a result, organizations are looking for an licensed, operational solution to achieve a wide network with a dynamic structure. A network that includes the following features:
SD-WAN architecture allows organizations to use internet connection for a wide network in addition to existing traditional connections and optimize the use of this network through intelligent routing. SD-WAN not only performs functions related to common wide area network connections, but also ensures secure transmission of application services in the most efficient manner. This technology, as a virtual overlay, allows you to define and automatically operate routing patterns through a single dashboard.
The licensed Cisco SD-WAN gives customers more flexibility. Now you can optimize your routing paths depending on your work priorities and bandwidth needs, as well as critical business applications. SD-WAN simplifies control for the customer and the wider network for management. SD-WAN compatibility does not mean migrating from MPLS or 4G/LTE. You can maintain the classic wide-area network structure for business-critical enterprise applications through MPLS-VPN, and then route the rest of the enterprise network traffic over the Internet to reduce costs.
It is used as a Network Management System (NMS) for SD-WAN. It provides real-time monitoring and notification, simplifies the implementation of changes in the network and provides a centralized view of the network. It supports web console, REST API, CLI, Syslog, SNMP and NETCONF.
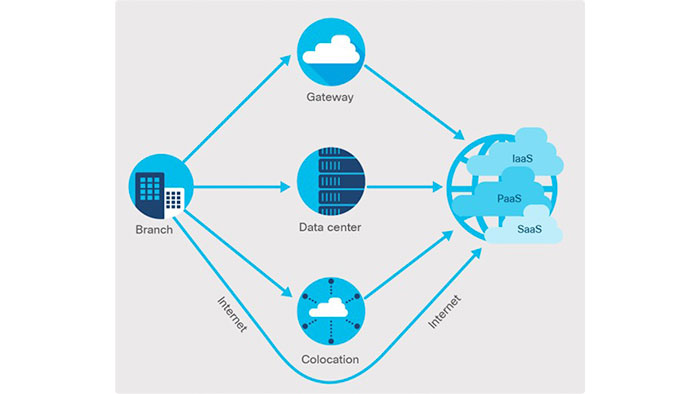
It is used as Switch Fabric and it can be any platform including MPLS, 4G/LTE, private fiber and Internet that establishes the connection between Management, Control Plane and Data Plane modules in SD-WAN architecture.
The service under Cisco’s Cloud is to provide Zero Touch functionality to customers. Cisco devices used at the edge (vEdges) automatically find the vBond of their network through ZTP, so to configure the device with the factory settings, it is only necessary to connect the device to the Internet.
It is responsible for the communication between the three layers of Management, Control and Data Plane. The first point is for authentication and authorizes all control connections through the whitelist model. Control Plane communication load balance is also in charge of the vBond server.
Physical or virtual routers are the edge of branches, data centers, remote sites and central offices that create a secure data plane in the SD-WAN network. Secure control plane synchronization through communication with vSmart controllers and implementation of application and data plane routing policies is the responsibility of vEdges.
It handles the implementation of Control Plane policies such as traffic engineering and partitions per VPN topology. It reduces the complexity within the network and manages and controls the synchronization of connections between all WAN edges.
SD-WAN architecture is based on the structure of modular routers. Routers have the following three components:
All communication between Control Plane and I/O modules is done through a platform called Switch Fabric.
It is responsible for processing and transmitting data packets. It obtains the necessary information for data transfer on physical ports from the Control Plane module.
Its main task is to process the packets of routing protocols and build the routing table. After creating the table, it provides the information to the I/O module.