
Cisco Advanced Malware Production can run on the top the network endpoints as part of the Cisco’s content security products like Cisco ASA secure firewalls, Firepower family, ESA and WSA appliances.
For leveraging Cisco AMP features on the network, First AMP connector which is a lightweight piece of software, gets deployed on Windows, MAC or Linux endpoints while the rest of it lives and operates in the public or on-prem private cloud. In addition, AMP cloud services are consisted of two distinct consoles. Cisco AMP management console which is what you can interact with in order to set up various policies to deploy to endpoints, plus, to see what is actually going on in the network. After that, there is a database which is where AMP keep track of everything.
In the way that the file reputation feature works in AMP, whenever a file gets accessed, executed, copied and moved on the endpoint, the AMP connector will calculate a file hash using the SHA-256 algorithm which will provide some context regarding to file characteristics.
So, Cisco AMP will send this context to the AMP cloud as a lookup for further detail about the file. If any information will be found in the database, AMP will come back with verdict, else it will add a new entry. The verdict or disposition, can be categorized in one of the following in AMP: Good or Benign, Bad or malicious and Unknown. If the file was unknown to the AMP cloud, it tries to connect and submit the file to Cisco Secure Malware Analytics or Threat Grid
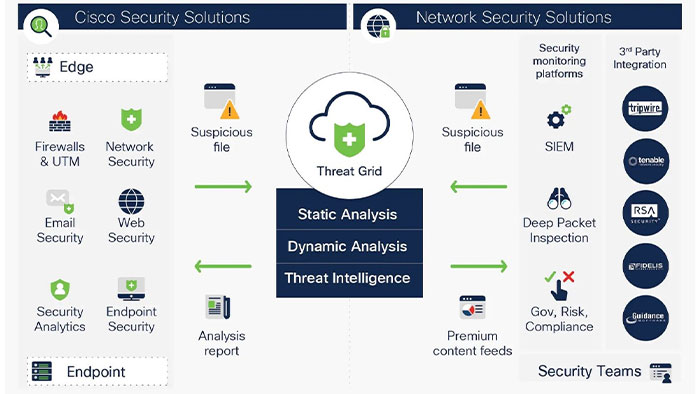
Cisco Threat Grid which can either be deployed on the cloud or on-prem, is where the file runs in a sandbox environment and then produces hundreds of indicators of behavior that it looks for to calculate an overall threat score which is a number between 0 and 100. Basically, any score higher that 95, is sufficiently deterministic that AMP database should be automatically updated. Therefore, instead of unknown, the unknown status changes to malicious. After that, the Cisco AMP retrospection comes into play. Retrospection event gets sent back to AMP on the endpoint and changes the disposition of the file to malicious. So, the file can then be blocked or quarantined on the endpoint it would be prevented from moving any further.