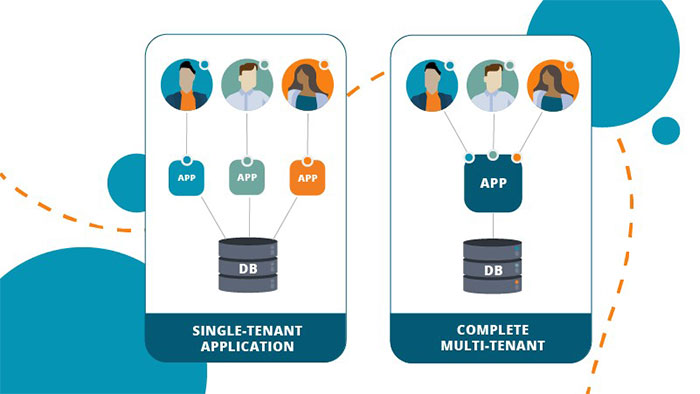
Multi-tenancy is an architecture where a single software application serves multiple customers. In multi-tenancy architecture, a single customer is called a tenant which may be given the ability to customize parts of the application. In summary:
Virtualization + Recourse Sharing = Multi-Tenancy
Multitenancy in cloud computing is basically resource sharing and some of the types of cloud computing services that exist are listed below:
In large organizations with multiple departments and branches, administering the network resources and user access may become a challenge. In multi-tenant data center, tenants subscribe to virtual data center (VDC), and based on the services hosted by the tenants within the virtual data center, each virtual data center can have multiple VN-Segments.
A virtual data center is a pool or collection of cloud infrastructure resources specifically designed for enterprise business needs. The basic resources are the processor, memory (RAM), storage (disk space) and networking (bandwidth).
In this model, Data centers have deployed VLANs to isolate the machines of different tenants on a single Layer-2 network and, with VRF, it can completely virtualize the Layer-2 and Layer-3 address spaces. Also, tenants might want to extend their IT services or storage network which uses non-IP protocols such as Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCOE).
Some advantages of multi-tenancy are:
• Same software version is available to all customers
• Global accessibility
• Software development and maintenance are done by the provider
• Provider hosted software is centrally located to be made easily accessible
Another important requirement for multi-tenant data center is to support the mobility of VMs within and across SPDC (Service Provider Data Centers) allows for dynamic tenant growth and maximizes resource utilization and sharing.
Up to 16 million virtual network segments (also called Virtual Network Identifiers) can be supported in VN-Segment network. In multi-tenancy architecture, tenant traffic can still be received as “Dot1Q” tagged that need to be classified to the VN-Segment assigned to those tenants.VN-Segment is the extension of VLANs– both need to coexist. VLAN range is from 1-4095 and VN-Segment(VNI) range is from 4096-16Million.
For VN-Segment deployment in the network, we can use the Cisco Nexus switches and the Cisco VXLAN. In this deployment, each VXLAN switch has a VTEP interface called a virtual interface or NVE interface. The NVE interface has one or more VNI’s bound to it and This is how the VTEP gets access to the LAN segments in the overlay.
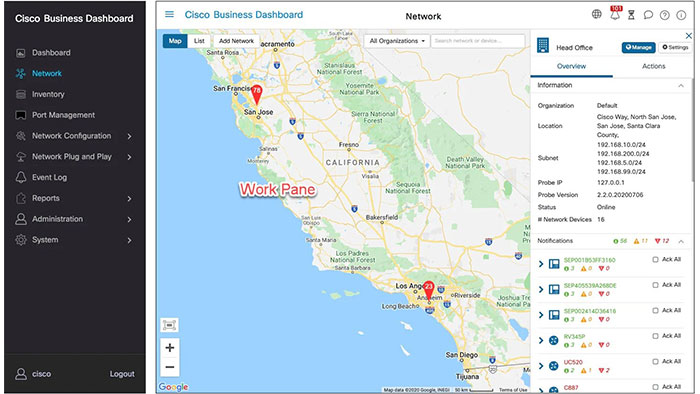
To address these challenges, a flexible and efficient multi-tenancy act is required to maintain a complex network. Cisco business dashboard introduces organizations support with multiple organizations, device groups and defined user roles.
Cross site management can be accomplished centrally for a specific organization, a network group or all devices. Flexible deployment options with different user roles and access rights are available as one software platform serves multiple organizations.