The new licensed Cisco FMC 7.2 (Firepower Management Center) is a comprehensive security management platform that allows network administrators to easily configure, monitor, and manage their security infrastructure. It is a key component of Cisco’s Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) solution, which combines the industry-leading security capabilities of Cisco ASA with the advanced threat detection and prevention features of Cisco FMC 7.2.
The licensed Cisco FMC 7.2 is designed to be deployed as a virtual appliance or on a physical server, depending on the specific requirements of the organization. It can be deployed as a standalone device or in a high-availability configuration for maximum uptime and redundancy.
The FMC 7.2 architecture is based on a distributed model, which allows for scalability and flexibility in managing large and complex security environments.
Policy-based routing (PBR) is a mechanism that allows you to selectively route traffic based on policies defined by the network administrator. PBR can be used to implement various routing policies such as load balancing, traffic prioritization, and routing based on application type. However, sometimes the default routing path may not be the most optimal one, and it may be necessary to monitor the performance of the available paths and switch to a better one when necessary.
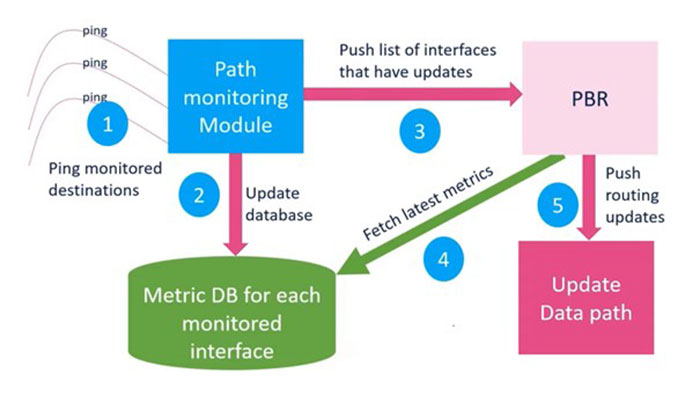
Path monitoring is a feature that allows you to monitor the status of a particular path and switch to an alternate path if the primary path fails or becomes congested. Path monitoring can be done using various methods such as ICMP, HTTP, or SNMP. In this article, we will use ICMP path monitoring to illustrate how to configure PBR with path monitoring in Cisco IOS.
PBR is a flexible tool that can be used to implement various routing policies such as load balancing, traffic prioritization, and routing based on application type. In Cisco FMC 7.2, PBR can be configured using access control policies (ACPs).
You can use PBR to implement various routing policies such as load balancing, traffic prioritization, and routing based on application type. PBR is a powerful tool that can help you optimize your network performance and ensure efficient use of your network resources.
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) is a Cisco proprietary routing protocol that is used to share routing information between routers within a single autonomous system (AS). EIGRP is designed to provide fast convergence and efficient use of bandwidth in large enterprise networks.
EIGRP is a classless routing protocol, which means that it supports variable-length subnet masks (VLSMs) and can advertise subnets of different sizes. EIGRP uses the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to calculate the shortest path to a destination network, and it supports load balancing across up to six equal-cost paths.
EIGRP uses a metric called “composite metric” to calculate the best path to a destination network. The composite metric takes into account bandwidth, delay, reliability, load, and maximum transmission unit (MTU) of the path. EIGRP also supports route summarization, which can help reduce the size of the routing table and conserve bandwidth.
EIGRP can be configured in Cisco FMC 7.2 (Firepower Management Center) using the Cisco IOS CLI (Command Line Interface) or the Cisco FMC 7.2 GUI. In Cisco FMC, you can configure EIGRP by creating an EIGRP routing instance, defining the network topology, configuring the EIGRP parameters, and enabling EIGRP on the appropriate interfaces.
In summary, EIGRP is a fast and efficient routing protocol that is designed for use in large enterprise networks. It supports VLSMs, load balancing, and route summarization, and it can be configured in FMC 7.2 to provide reliable and efficient routing within a single autonomous system.